 – Thierry, you are one of the best map readers I have ever seen. But if you want to become the best, you must change your way of orienteering. You have to start building much simpler mental images of the terrain if you want to become faster. This was the message from Börje Vartiainen – Kalevan Rasti’s coach – to Thierry Gueorgiou in the autumn of 2001, at a time when Gueorgiou was in his deepest valley yet as an orienteer.
– Thierry, you are one of the best map readers I have ever seen. But if you want to become the best, you must change your way of orienteering. You have to start building much simpler mental images of the terrain if you want to become faster. This was the message from Börje Vartiainen – Kalevan Rasti’s coach – to Thierry Gueorgiou in the autumn of 2001, at a time when Gueorgiou was in his deepest valley yet as an orienteer.
WOC 2001: Breakdown of a dream
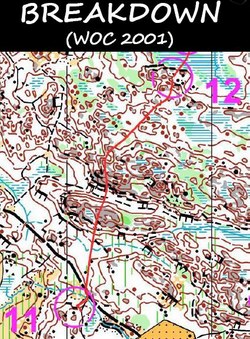
To recap from part I of this article series from Thierry Gueorgiou’s presentation at the Norwegian O-gala – Thierry’s “breakdown” was after a very disappointing 18th place at the short distance in the World Orienteering Champs in Finland in a close to mistake-free race. After many years of believing strongly that he could be the World Champion, Thierry had, for the first time, admitted to himself that maybe he would not be a World Champion after all (map example to the right – Vattula 2, WOC 2001, short distance final, Ari Anjala & Reijo Kujansuu).
– My technique is slow
Vartiainen’s message helped Thierry onto the right track. – The 2002 season was my rebirth as an orienteer, Thierry comments. A new technique, a new attitude and mental preparations were the key elements in this process.

As an excellent map reader already at that time, Thierry read all these details accurately and fast.
So what was the problem with the old technique? Let us take a look at one of Thierry’s examples on a fantasy map (below) for an illustration of the old technique. Following along the drawn route choice, you read the map passing the marsh, then the tree root, the cliff, then between the two hills, cross the small track, then the small cliff, and so on. As an excellent map reader already at that time, Thierry read all these details accurately and fast – running in full control from feature to feature.

And the problem? Even if you run fast and orienteer fast – reading all details takes extra time.
I don’t know if this is the right way to go, but it is a fact.
Thierry: – Maps get more and more detailed. I don’t know if this is the right way to go, but it is a fact. My new orienteering technique had to account for this. Also, there are different mapping styles. Different mappers give very different maps. And there is a large range of different terrain types. I had to try to find a general method anyway.
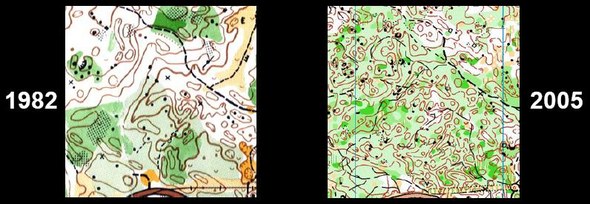
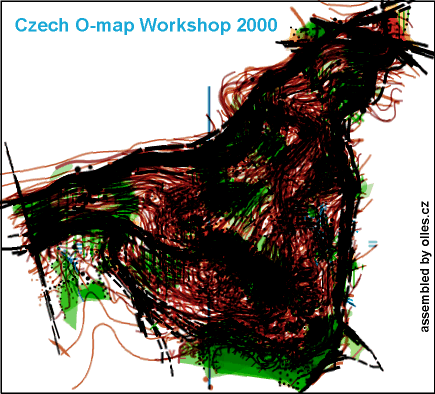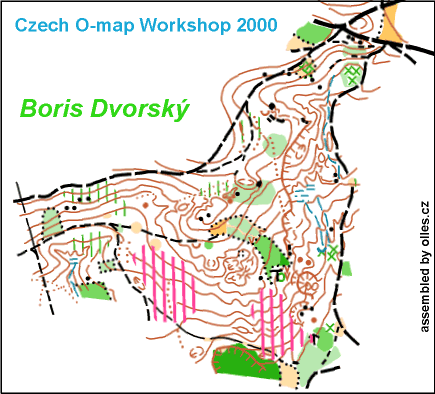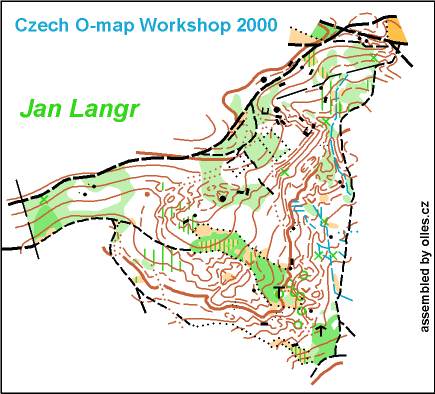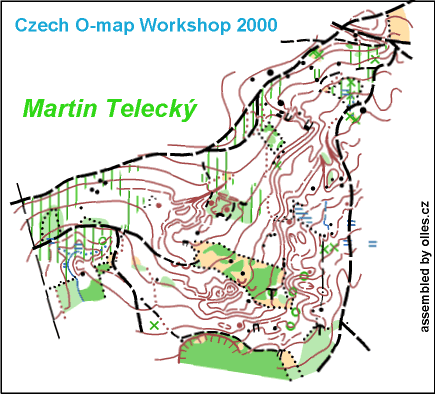
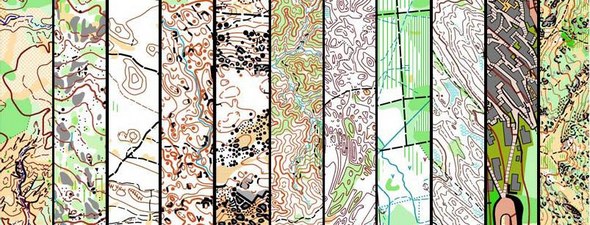
Upper: Mapping evolution from 1982 to 2005 in WC Final 2006 area. Middle: 16 mappers – 16 maps – animated image from Olles.cz. Lower: Maps from different terrain types.
 Visibility
Visibility
It is obvious – and most orienteers make use of it in every race: Use the most visible and distinct features as key points in your orienteering. But how far do you go in your analysis of visibility and distinctness of features? Do you analyze visibility and distinctness for all features before planning your route choice, and create a “visibility map” in your head?
Thierry [see map to the right]: – We can mark the areas from which we can see this control on the map. We can see the control from the hills, from this yellow area and from a part of the marsh.
But how far do you go in your analysis of visibility and distinctness of features?
These kinds of visibility maps are at the heart of Thierry’s new orienteering technique. Another example from Thierry’s presentation: The map below show visibility maps for two different features. The blue visibility map is for feature A, a stone in a small re-entrant. The red visibility map is for a large hill. Thierry again: – The stone you can see from only a very small area. The hill you can see from a large area.
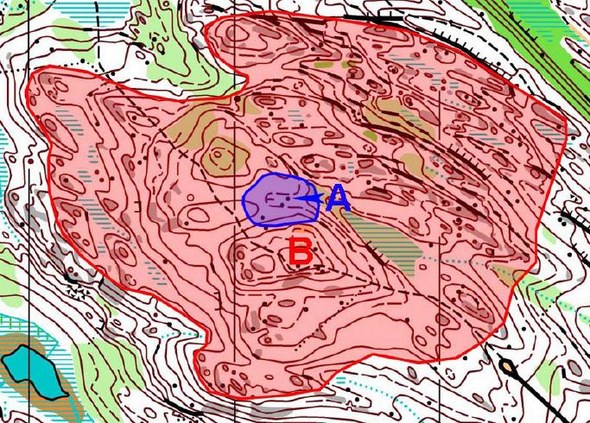
Map: Ruläys, Rauno Asikainen
Distinct features
– You must identify the remarkable features.
Thierry again: – The next question I asked myself is what is important on a map. For this question, there is no general answer. This is different from terrain type to terrain type. – You must identify the remarkable features. The features which are both isolated and visible! Again – let’s use two of Thierry’s examples. The first example (to the left below) is for a special open French terrain with a lot of cliffs. As these cliffs are visible from far away, it would be tempting to base much of the orienteering on them. However, there is another set of details in this terrain type which are much more remarkable and isolated: Big characteristic trees (green ring on the map). The second example (Finnish terrain, to the right below) is very different. Here the cliffs are the remarkable and characteristic details which you can base your navigation on.
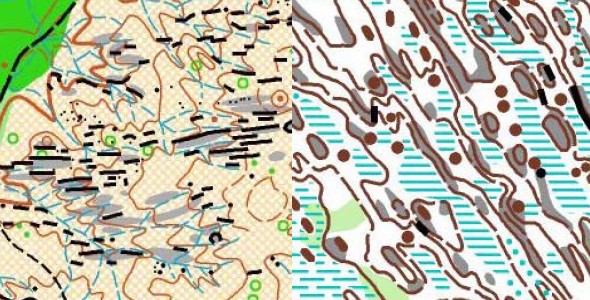
Left map: LES AUREDES, Pellegry Alain & Laurent. Right map: TAHKOVAARA, Rauno Asikainen, Jussi Silvennoinen & Börje Vartiainen
In short: Don’t use stones as a basis for your navigation in an area full of stones.
– Sometimes a contour line can be really like a motorway.
Visible and distinct features
We are nearly there – but what about all those different terrain types? – Contour details like hills and depressions are visible and distinct in many terrain types – they are usually a very good to use for this technique, is Thierry’s tip to all the Norwegian listeners at the O-gala. – Sometimes a contour line can be really like a motorway. All you have to do is to follow it, Thierry commented the second leg on this years World Orienteering Champs middle distance. Further key points in all terrain types are (1) thrust your compass and (2) keep your head high. Also – and this is the main point – when using these visible and distinct features for your navigation, you can (and must) ignore all the other details. This is what makes you fast! (But don’t narrow the technique too much, or you will end up like Thierry Gueorgiou in the World Champs middle distance in 2006 – a miserable number four…)
“Full speed – no mistake”
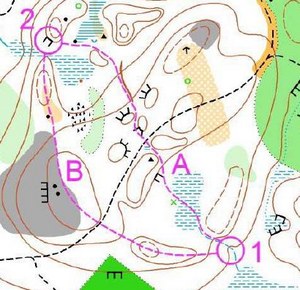
Thierry: – The equation to solve is higher speed at lower risk. Piecing the above elements together, we arrive at what Thierry calls the “Full speed – no mistake” technique. Let us go back to the first example, and see how Thierry solves it with the “Full speed – no mistake” technique (map to the right). Thierry: – There is one perfect solution for every leg which you must find. The “Full speed – no mistake” technique helps you to find the optimal route choice. Runner A knows where he is – runner B knows where to go.
Let us analyze the leg and the two route choice alternatives using visibility maps (not shown explicitly). Along route choice alternative B, the visibility area for all three hills along the route choice is very good – so good that you can see from hill to hill, and maintaining full speed all the way. Along route choice A, you can argue that the first hill/cliff along the route choice is distinct and visible from quite a large distance.
You need to – again extremely fast – be able to visualize the terrain in 3D in your head from the physical map.
However, it is not visible from control number one, and thus lower speed and more orienteering is necessary for the first part of the leg. The next cliff you pass is again a nice, distinct feature, but visibility from the direction of the runner is rather limited. Visibility and distinctness for the rest of route choice A is also poorer than for route choice B.
See in 3D
What is needed to apply this technique effectively, is the ability to extremely fast get from the physical map to a visibility map for all distinct points in the terrain. To do this, you need to – again extremely fast – be able to visualize the terrain in 3D in your head from the physical map – as the 3D terrain model is the natural step to get from physical map to visibility map.

Master the technique
In the simple example above, this looks obvious. But let us take a look at a few of Thierry’s examples which are not that obvious. Both are from the World Cup Final in 2006 in France (Map: AYDAT, O’vert4) – a terrain which nobody masters as well as Thierry Gueorgiou.
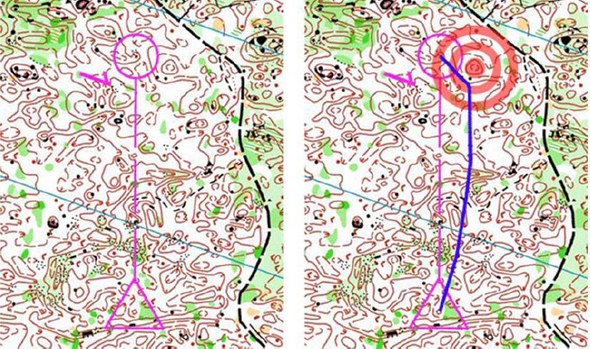
Here it is not that obvious which features are distinct and visible. At first look, everything looks just the same, and it is tempting to use the round cliff just left of the line as your attack-point for the control, as it (a) looks like a distinct feature and (b) you have a good entrance to the control over the small hill between the cliff and the control.
A small error in compass bearing can be tolerated, and maximum speed can be held until close to the control.
However, when we look at visibility maps (not shown), we see that the cliff is only visible from a small area, and you might miss it if your compass bearing is not very accurate. OK you could say – “Let us take the hill just behind the round cliff. That is larger, and my compass bearing needn’t be that accurate.” But again visibility is an issue: Both the round cliff and the small hill to the right of the round cliff are “in the way”.
Let us take a look at Thierry’s approach: The hill just to the right of the control (marked with three red rings in the right part of the above figure). Due to the large flat area south of the hill, the hill is visible from a large region along the route the runner is coming from. Thus, a small error in compass bearing can be tolerated, and maximum speed can be held until close to the control.
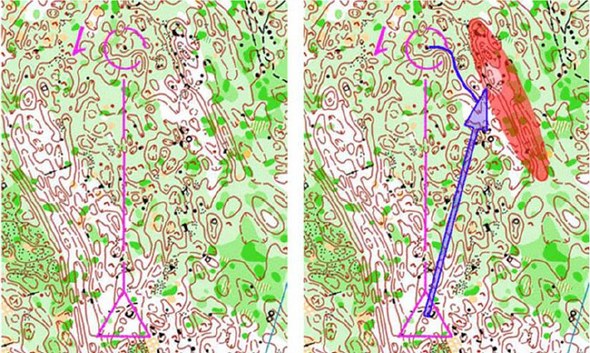
Below you see the second example from the World Cup Final. Again, visibility and distinctness is the key – this time for the hill to the right of the leg:
Training and attitude
Training yourself to master the method…
The “full speed – no mistake”-technique outlined above is one thing – and in itself you might say it is nothing special. Similar ideas lie behind most elite-orienteers technique – even if it might not always be spelled out this clearly regarding visibility maps and tactics. Training yourself to master the method, having the correct attitude and – last but not least – the mental aspect, is something completely different! More about this in the next article in this series.

 World of O News
World of O News
Very good article :)
I like the ‘tips’ and the ideas that Thierry sharing with us!
Please give us more articles like this one!
J.
These articles are great. Thank you very much for them Jan! Looking forward to reading next part.
Wow, great article! Cool method Thierry adopts. I’ll try it out ;)
INCREDIBLE! That method looks really good. Think i’m gonna try it to.
Are the visibility maps mentioned in the article shown somewhere in the internet? Very interesting way of thinking route choices!